Given data:
* The mass of the skier is m = 55 kg.
* The angle of the slope is,
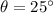
* The initial velocity of the skier at the top is,
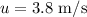
* The coefficient of friction between the ski boot and slope is,
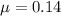
* The distance traveled by the skier along the inclined plane is,
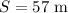
Solution:
The diagrammatic representation of the given case is,
The angle of the inclined plane with the vertical axis is,
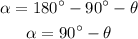
Thus, the component of the weight of skier along the inclined plane is,
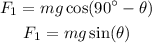
where g is the acceleration due to gravity,
Substituting the known values,
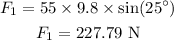
The component of weight perpendicular to the inclined plane is,
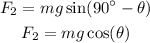
Substituting the known values,
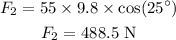
From the diagram, the normal force acting on the skier is,
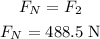
The frictional force acting on the skier in terms of the normal force is,
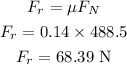
Thus, the net force acting on the skier down the inclined plane is,
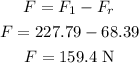
According to Newton's second law, the acceleration of the skier is,
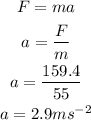
By the kinematics equation, the speed of the skier after moving to distance S is,
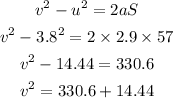
By simplifying,
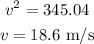
Thus, the speed of the skier after moving 57 m downhill is 18.6 meters per second.