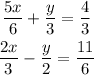
to solve this,
Step 1
the purpose of this method is eliminate a variable by adding the two equations, to do this, you need to be sure that the add will make that variable disappear.
Let's see y
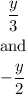
to eliminate y make
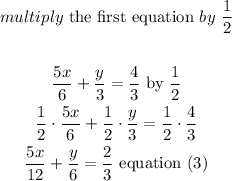
Now, multiply the second equation by 1/3
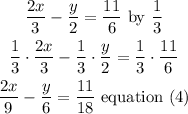
Now, add equations 3 and 4
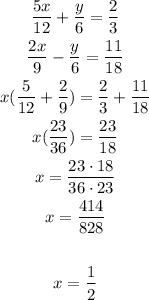
Now, with this value of x, find y, replacing in the equation 1 or 2
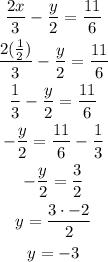
so, the solution is x=0.5 and y =-3
I really hope this helps