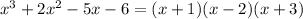Solving a third-degree equation implies testing some possible solutions until we find them all.
The equation to solve is:
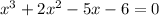
Dividing the factors of the independent coefficient by the factors of the leading coefficient will give us some candidates solutions:
+/- 6, +/-3, +/- 2, +/- 1
Testing x = -1
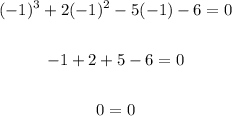
The equation is verified, so x = -1 is a solution.
Testing x = 1
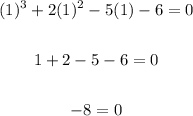
The equation does not verify, so x = 1 is not a solution.
Testing x = 2
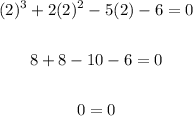
x = 2 is a solution.
Finally, testing x = -3
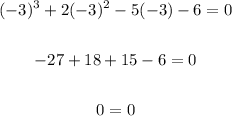
The real zeros are x = -1, x = 2, x = -3.
Factoring: