Answer:
17.6 L.
Step-by-step explanation:
What is given?
Mass of oxygen (O2) = 12 g.
Molar mass of O2 = 32 g/mol.
Temperature (T) = 25 °C + 273 = 298 K.
Pressure (P)= 52.7 kPa
R = 0.082 L*atm/mol*K.
What do we need? Volume.
Step-by-step solution:
We have to use the following formula of ideal gas law:
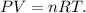
Where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number ofmoles, R is the constant of ideal gas and T is tthe emperature ion the Kelvin scale.
But we have to convert 12 g of O2 in moles, so let's do this using the molar mass of O2:
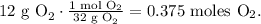
Now, we have to find the pressure in units of atm. Remember that 1 atm equals 101.3 kPa:
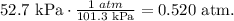
And the final step is to solve for 'V' which is volume and replace the given data:
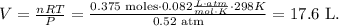
The volume of oxygen gas would be 17.6 L.