Last week run distance = 32 miles
Increased amount this week = 6.4 miles
We have to find the percentage of increase.
Thus, we divide the increase (which is 6.4) by the original length he ran last week (which is 32).
Then,
We multiply the answer by 100.
Let's do this:
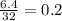
Now,
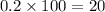
The answer is 20%
Answer: C