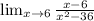
Complete the table: Substitute the x in the equation for the given value and find the value of y:
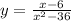
![\begin{gathered} y=(5.9-6)/((5.9)^2-36)=(-0.1)/(34.81-36)=(-0.1)/(-1.19)=0.08403 \\ \\ y=(5.99-6)/((5.99)^2-36)=(-0.01)/(35.8801-36)=(-0.01)/(-0.1199)=0.083402 \\ \\ y=(5.999-6)/((5.999)^2-36)=(-0.001)/(35.988001-36)=(-0.001)/(-0.011999)=0.0833402 \\ \\ y=(6-6)/((6)^2-36)=(0)/(36-36)=(0)/(0)=\text{undefined} \\ \\ y=(6.001-6)/((6.001)^2-36)=(0.001)/(36.012001-36)=(0.001)/(0.012001)=0.083326 \\ \\ y=(6.01-6)/((6.01)^2-36)=(0.01)/(36.1201-36)=(0.01)/(0.1201)=0.083263 \\ \\ y=(6.1-6)/((6.1)^2-36)=(0.1)/(37.21-36)=(0.1)/(1.21)=0.082644 \end{gathered}]()
-------------------------
With the data of the table you can see that the limit when x tends to 6 is 0.083 (or 1/12). You can get an accurate answer to the limit as follow:
To find the limit multiply numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the numerator (x+6):
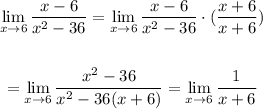
Then, evaluate the limit with x=6:
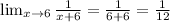
The limit is 1/12
------------------------------