ANSWER:
![\begin{gathered} ((x+5)^2)/(5^2)+((y-2)^2)/(2^2)=1 \\ \text{end points of the major axis }=(0,2),(-10,2) \\ \text{end points of the minor axis }=(-5,4),(-5,0) \\ f=(-5+\sqrt[]{21},2),(-5-\sqrt[]{21},2) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/mhz2tz4eyr9l5nv9ml9pgbzvk7avy1slxh.png)
Explanation:
We have the following equation of the ellipse in its standard form:
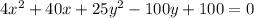
We convert this equation to the general form of an equation of an ellipse with no center at the origin, like this:
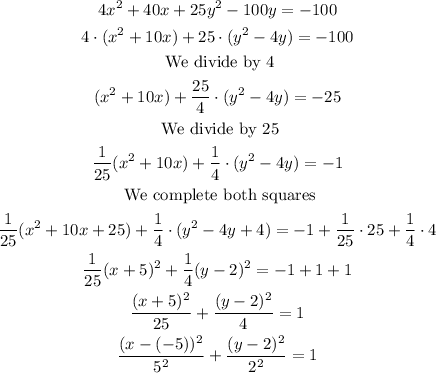
We have that the equation in its general form is the following:
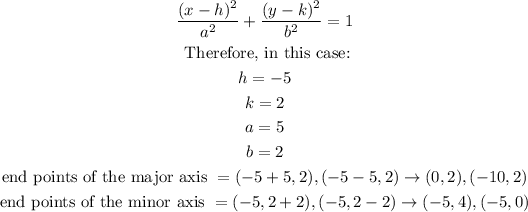
Now, we calculate the focus of the ellipse just like this:
![\begin{gathered} c^2=a^2-b^2 \\ c=\sqrt[]{5^2-2^2} \\ c=\sqrt[]{25-4} \\ c=\sqrt[]{21} \\ \text{ Therefore, the foci is:} \\ f=(-5+\sqrt[]{21},2),(-5-\sqrt[]{21},2) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/fvaruevfze7p5d37xc3riyz8llkyx2zcat.png)