Step 1: Using the theorem of binomial distribution
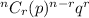
n = 13
p = probability that the baby is a girl
q = probability that the baby is not a girl
Step 2: To find the probability that most eleven of the thirteen babies are girls
= 1 - [(probability that exactly twelves girls) + (probability that exactly thirteen girls)]
Step 3: Get the value of p and q

Step 4: Find the probability that at most eleven of the thirteen babies are girls.
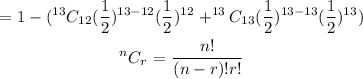
Step 5: Simplify the expression
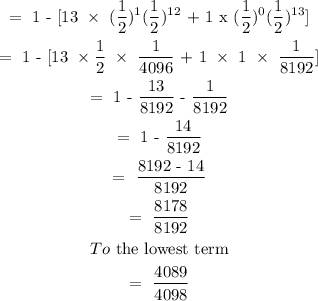
Option B is the correct answer