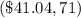Summarizing the information:
Price: $75 => Demand: 25
Price: $20 => Demand: 100
Price: $50 => Supply: 100
Price: $25 => Supply: 20
a.
To calculate the demand function, we identify at least two points of the demand line. Using the information given by the problem, these two points are:
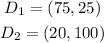
Given the slope formula:
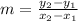
Where:
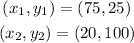
Then:
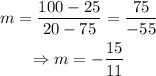
Now, by the slope-intercept form of the line equation (and using the point D₁):
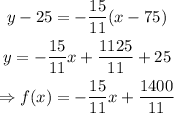
And that is the demand function.
b.
We identify two points of the supply line:
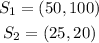
The slope of the line is:
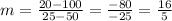
Now, by the slope-point form of the line (using S₁):
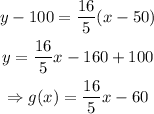
Where g(x) is the supply function.
c.
To find the equilibrium point, we solve the equation f(x) = g(x):
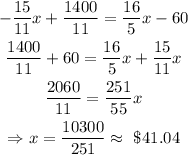
Now, we find the corresponding quantity:
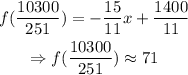
The equilibrium point is: