In order to find the direction of the initial velocity, first let's calculate the change in velocity caused by the acceleration:
![\begin{gathered} F=m\cdot a\\ \\ 2655=15.5\cdot a\\ \\ a=171.29\text{ m/s^^b2}\\ \\ \\ \\ \Delta V=a\cdot t\\ \\ \Delta V=171.29\cdot0.05\\ \\ \Delta V=8.5645\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}]()
Now, let's calculate the horizontal and vertical components of the final velocity.
The direction is N45W, therefore the angle is 90° + 45° = 135°:
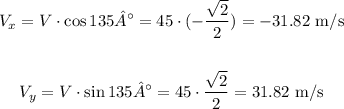
The change in the velocity occurred in north direction, so let's calculate the initial vertical velocity:
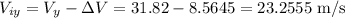
Now, to calculate the direction, we can use the arc tangent below:
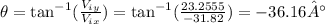
Since the direction is between north and west, we need to add 180° to the result, so the angle will be 143.84°.
This angle is equal to the direction N 53.84° W.