SOLUTION
Step 1: Definition of Trigonometry
Trigonometry is one of the important branches in the history of mathematics that deals with the study of the relationship between the sides and angles of a right-angled triangle. In trigonometry, the angles can be either measured in degrees or radians. Some of the most commonly used trigonometric angles for calculations are 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°.
Step 2: State the three trigonometric ratios
The trigonometric ratios of a triangle are also called the trigonometric functions. Sine, cosine, and tangent are 3 important trigonometric functions and are abbreviated as sin, cos and tan.
Step 3: Show how these ratios or functions, evaluated in case of a right-angled triangle.
Consider the right-angled triangle above, where the longest side is called the hypotenuse, and the sides opposite to the hypotenuse are referred to as the adjacent and opposite sides.
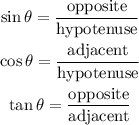
STEP 4: Evaluate the other 3 ratios that can be derived from the given ratios in step 3

Knowing .these ratios are the basic concepts of Trigonometry.