We are given that an object falls with an acceleration of -6 miles/h/s. To determine the initial velocity we will use the following motion:
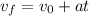
Where:
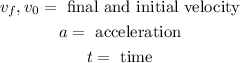
Now, we solve for the initial velocity by subtracting "at" from both sides:
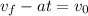
Now, we plug in the values:
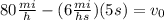
Now, we solve the operations:
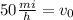
Therefore, the initial velocity is 50 mi/h.