The locations where the passneger travels can be shown as,
The position of passenger at city A can be expressed as,
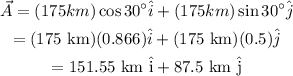
The position of passenger at city B can be expressed as,

The position of passenger at city C can be expressed as,
![\begin{gathered} \vec{C}=(99.22km-195km)\hat{i}+231.32\operatorname{km}\hat{j}_{} \\ =-95.78\text{ }\hat{\text{i}}+231.32\text{ km}\hat{\text{j}} \end{gathered}]()
Therefore, the magnitude of distance of city C can be calculated as,
![\begin{gathered} C=\sqrt[]{(-95.78km)^2+(231.32km)^2} \\ =\sqrt[]{9173.81km^2+53508.94km^2} \\ =252.3\text{ km} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/high-school/mz6pjhu2znqzkgrhwz9afqbm5fo4hss7tt.png)
Thus, the distance of city C from point O is 252.3 km.
The direction of location is calculated as,
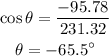
Thus, the direction of city C from point O is -65.5 degree.