The next equation models the height (h) of the frisbee in the air as a function of time (t):
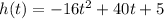
First, we need to find how long is the frisbee in the air. To do this we have to find the zeros of the above function. Applying the quadratic formula with a = -16, b = 40, and c = 5 (the coefficients of the function), we get:
![\begin{gathered} t_(1,2)=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a} \\ t_(1,2)=\frac{-40\pm\sqrt[]{40^2-4\cdot(-16)\cdot5}}{2\cdot(-16)} \\ t_(1,2)=\frac{-40\pm\sqrt[]{1920}}{-32} \\ t_1\approx(-40+43.82)/(-32)\approx-0.12 \\ t_2\approx(-40-43.82)/(-32)\approx2.62 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/9bkvx45qtm5lxw25gw613dafbvahvyrcxc.png)
Given that variable t measures time, then t1 = -0.12 is discarded. In consequence, the frisbee is in the air for 2.62 seconds.
Substituting with t = 0 into the equation:
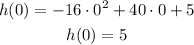
This means that after 0 seconds the height of the frisbee is 5 ft
Substituting with t = 1 into the equation:
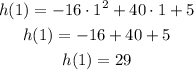
After 1 second the height of the frisbee is 29 ft
Substituting with t = 2 into the equation:
After 2 seconds the height of the frisbee is 21 ft
Finally, after 2.62 seconds the height of the frisbee is 0 ft