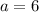We are given that the position of an object if given by the following equations:
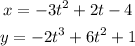
To determine the velocity we will determine the derivative of each of the functions. For "x" we have:
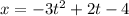
Finding the derivative with respect to time we get:
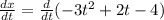
Now we distribute the derivative on the left side:
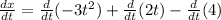
For the first derivative we will use the rule:
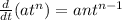
Applying the rule we get:
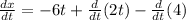
For the second derivative we use the rule:
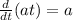
Applying the rule we get:
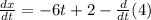
For the third derivative we use the rule:
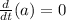
Applying the rule we get:
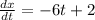
Now, since the velocity is the derivative with respect to time of the position and this is and we determine the derivative for the x-position what we have found is the velocity in the x-direction, therefore, we can write:
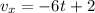
Now we substitute the value of time, t = 1, we get:
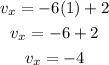
Now we use derivate the function for "y":
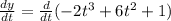
Using the same procedure as before we determine the derivative:
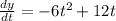
This is the velocity in the y-direction:
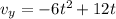
Now we substitute the value of t = 1:
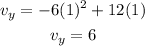
Now, the speed is the magnitude of the velocity, the magnitude is given by:
![v=\sqrt[]{v^2_x+v^2_y}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/b1061y4obi6re8od41e46k9muims0av3n1.png)
Substituting the values we get:
![v=\sqrt[]{(-4)^2+6^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/24zlajewu44am3ztlvw6wk63s96tpk6xgc.png)
Solving the operations:
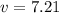
Therefore, the speed is 7.21 m/s.
To determine the acceleration we will determine the derivative of the formulas for velocities:
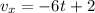
Now we derivate with respect to time:
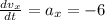
Now we use the function for the velocity in the y-direction:
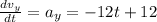
Now we substitute the value of t = 1:
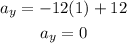
Since the acceleration in the y-direction is zero, this means that the total acceleration is the acceleration in the x-direction, therefore, the magnitude of the acceleration is: