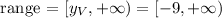The equation is
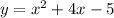
We can already find the vertex using the vertex formulas
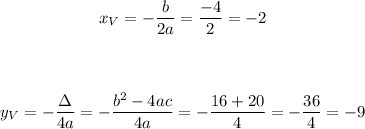
Therefore the vertex is
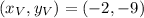
Now we have the vertex we also have the axis of symmetry and the max/min of the function, in that case, it's a minimum because a > 0. Therefore
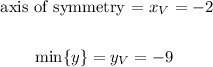
We can find the x-intercept easily
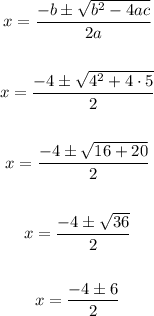
Hence
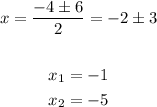
The y-intercept is just the c value, then it's -5.
Now we can do the domain, there's no restriction for parabolas in the domain, then
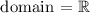
And the range is