In order to calculate the angular acceleration, we can use the following formula:
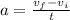
Where vf is the final angular speed, vi is the initial angular speed and t is the interval of time.
Since the speed is in rev/min, we need to convert to rad/s.
Knowing that 1 rev = 2π rad and 1 min = 60 s, we have:
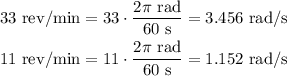
Now, using vf = 1.152, vi = 3.456 and t = 2, we have:
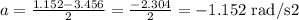
So the angular acceleration is -1.152 rad/s².