Identity equations are always true, no matter the values that the variables take.
We have to calculate for each one, and if the result gives a true statement, then the equation is an identity:
1) 3(x - 1) = x + 2(x + 1) + 1
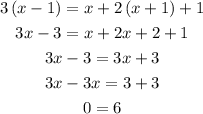
This is FALSE (for any value of x), so the equation is not an identity.
2) x-4(x + 1) = -3(x + 1) + 1
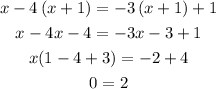
This is FALSE, so the equation is not an identity.
3) 2x + 3 = 1 (4x + 2) + 2
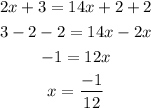
This equation holds true only for x=-1/12, so it is not an identity.
4) (6x - 3) = 3(x + 1) – x-2
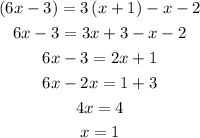
This equation holds true only for x=1, so it is not an identity.
Neither of the options is an identity.