Given that tan theta = 4/3 and theta lies in the third quadrant.
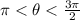
Divide the compound inequality by 2.
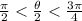
This means theta/2 lies in the second quadrant. So, cos theta/2 and sec theta/2 are negative.
Use trigonometric identities to find sec theta.
![\begin{gathered} \sec \theta=\sqrt[]{1+\tan ^2\theta} \\ =\sqrt[]{1+((4)/(3))^2} \\ =\sqrt[]{1+(16)/(9)} \\ =\sqrt[]{(25)/(9)} \\ =-(5)/(3) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/qpq2j22f5z3yueq5lbudgrfikbspbmwelc.png)
we know that cosine is the inverse of secant. So, cos theta = -3/5.
now, using the half-angle formula, we have to find cos theta/2,
![\begin{gathered} \cos ((\theta)/(2))=-\sqrt[]{(1+\cos x)/(2)} \\ =-\sqrt[]{(1-(3)/(5))/(2)} \\ =-\sqrt[]{((2)/(3))/(2)} \\ =-\sqrt[]{(1)/(3)} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/m92dyd9ecua9oxa5upy488qd0ro6xnxzw1.png)