5.
Given the equation to solve for x:
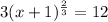
The steps for the solution are as follows:
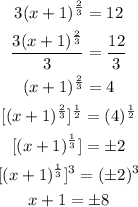
From the above equation, we have x + 1 = 8 and x + 1 = -8. These imply x = 7 and x = -9.
Check for extraneous solutions:
If x = 7, then the left-hand side of the equation is:
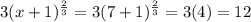
Thus, the equation holds true at x = 7.
If x = -9, then the right-hand side of the equation is:
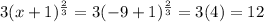
Thus, the equation holds true at x = -9.
There is no extraneous solution. The solutions of the given equation are x = 7 and x = -9.
6.
Given an equation to solve for x:
![\sqrt[]{3x+2}-2\sqrt[]{x}=0](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/gyr93lc8qqosz8dtb2gopxlp85629wdxis.png)
The steps of the solution are as follows:
![\begin{gathered} \sqrt[]{3x+2}-2\sqrt[]{x}=0 \\ \sqrt[]{3x+2}=2\sqrt[]{x} \\ (\sqrt[]{3x+2})^2=(2\sqrt[]{x})^2 \\ 3x+2=4x \\ 2=4x-3x \\ 2=x \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/72gc7awo5b9rug4m76r9osdl6mv9z80n5h.png)
Thus, the solution of the equation is x = 2.