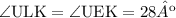∠KU and ∠LE are vertically opposite angles, which means that they are congruent, so that:
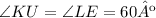
∠LUE and ∠LKE intersect the same arc mLE, which means that they are congruent:
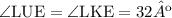
∠KU and the vertex angle marked in blue are supplementary angles, which means that they add up to 180º:
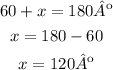
Knowing two of the three angles of the upper triangle, you can calculate the measure of the missing one, ∠ULK:
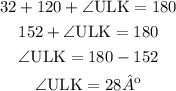
∠ULK and ∠UEK intercept the same arc mKU, so they are congruent: