To solve the question we will assume that the gas behaves like an ideal gas, that is to say, that there is no interaction between the molecules. Assuming ideal gas we can apply the following equation:
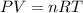
Where,
P is the pressure of the gas
V is the volume of the gas
n is the number of moles
R is a constant
T is the temperature
Now, we have two states, an initial state, and a final state. The conditions for each state will be.
Initial state (1)
P1=975Torr=1.28atm
V1=3.8L
T1=-18°C=255.15K
Final state(2), STP conditions
P2=1atm
T2=273.15K
V2=?
We will assume that the number of moles remains constant, so the nR term of the first equation will be constant. For each state, we will have:
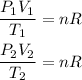
Since nR is the same for both states, we can equate the equations and solve for V2:
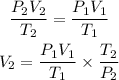
We replace the known values:
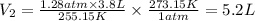
At STP conditions the gas would occupy 5.2L. First option