A circle can be represented by the following equation:
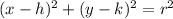
Where the radius is r and the center is (h, k).
Using the radius 6 and the center (3, -5), we have that:
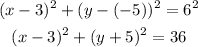
So the equation of the circle that satisfies radius = 6 and center = (3, -5) is:
(x-3)^2 + (y+5)^2 = 36