First Part 45-45-90 Triangle
first triangle
where the two angles different to 90° are same, the measure of the legsof the triangle are the same
then
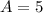
and to calculate B or the hypotenuse we use pythagoras
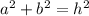
where a and b are legs and h the hypotenuse
replacing
![\begin{gathered} 5^2+5^2=h^2 \\ 25+25=h^2 \\ 50=h^2 \\ h=\sqrt[]{50} \\ h=5\sqrt[]{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/iza3y9gfay999vrha78pwjq63qhir14qc5.png)
the hypotenuse or B is
![B=5\sqrt[]{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/77cnx4meck978ugat2mess4xiusl42ygd1.png)
Second triangle
legs of the triangle have the same value then if we apply pythagoras
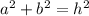
and replace the legs with the same value(a)
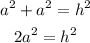
we can replace the hypotenuse and solve a
![\begin{gathered} 2a^2=(3\sqrt[]{2})^2 \\ 2a^2=18 \\ a^2=(18)/(2) \\ \\ a=\sqrt[]{9} \\ a=3 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/g54r1ecvyg6ddeuq1thbph42f4gyxmbrkf.png)
value of each leg is 3 units, then
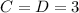
Second part 30-60-90 triangle
First triangle
we use trigonometric ratios to solve, for example I can use tangent for the angle 60 to find E
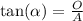
where alpha is the angle, O the oppiste side of the angle and A the adjacet side of the angle
using angle 60°
![\begin{gathered} \tan (60)=(E)/(6) \\ \\ E=6\tan (60) \\ \\ E=6\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/yv1a6f3e9qkqu5zv0twg00hgwg9sjatc66.png)
now using sine we calculate F or the hypotenuse
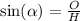
where alpha is the angle, O the opposite side from the angle and H the hypotenuse
using angle 60°
![\begin{gathered} \sin (60)=(E)/(F) \\ \\ F=(E)/(\sin (60)) \\ \\ F=\frac{6\sqrt[]{3}}{\sin (60)} \\ \\ F=12 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/tbpnv0v3w13g16i4t4b9thmce38p6rar48.png)
Second triangle
we use sine with 60° to find H
![\begin{gathered} \sin (\alpha)=(O)/(h) \\ \\ \sin (60)=(H)/(20) \\ \\ H=20\sin (60) \\ H=10\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/zjnpkd0fe6giw2i907vaf8a4kx5nihb2ii.png)
use cosine with 60° to find G
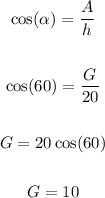
Final Values
![\begin{gathered} A=5 \\ B=5\sqrt[]{2} \\ C=3 \\ D=3 \\ E=6\sqrt[]{3} \\ F=12 \\ G=10 \\ H=10\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/daq6522hi2zan3zjoqp4nifzefk365ro9f.png)