Answer
![\Delta H_(rxn)\operatorname{\degree}=-4791.6\text{ }kJ\text{/}mol]()
Step-by-step explanation
The given chemical equation for the reaction is:
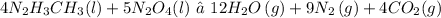
From the given table and question, the enthalpies of formation of the reactants ad products are:
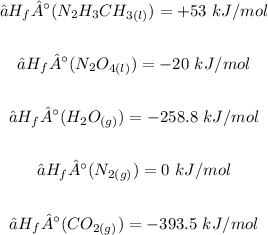
The ∆H° for this reaction can be calculated using the formula below:
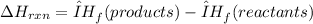
Put the each enthalpy of formation of the reactants and the products into the formula:
![\begin{gathered} \Delta H_(rxn)\degree=[12(-258.8)+9(0)+4(-393.5)]-[4(+53)+5(-20)] \\ \\ \Delta H_(rxn)\degree=[-3105.6+0-1574]-[212-100] \\ \\ \Delta H_(rxn)\degree=-4679.6-112 \\ \\ \Delta H_(rxn)\degree=-4791.6\text{ }kJ\text{/}mol \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/mrz90tt9phfn3609zirbed0sxzlw5vbcry.png)
Therefore, the ∆H° for this reaction is -4791.6 kJ/mol.