To know the empirical formula we will determine how many moles of each element we have. To do this, we must look up in the periodic table the atomic weight of each element.
The atomic weight of Ni = 58.6934 g/mol
O = 15.999 g/mol
Now we divide the mass of each element by its atomic weight to determine how many moles are in the sample.
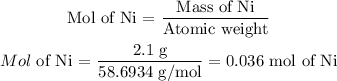
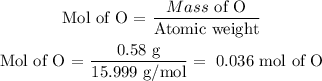
In the sample, there are 0.036 moles of oxygen and 0.036 moles of Ni. The ratio is 1 to 1, so the empirical formula will be: NiO