the Given the simultaneous equations
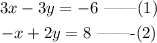
Solving the above equations by substitution method:
Step 1:
From equation 2, make x the subject of the formula
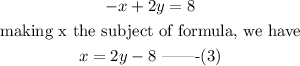
Step 2:
Substitute equation 3 into equation 1
![\begin{gathered} \text{From equation,} \\ 3x-3y=-6 \\ \text{Thus, we have} \\ 3(2y-8)-3y=-6 \\ \text{opening the brackets, we have} \\ 6y-24-3y=-6 \\ \text{collecting like terms, we have} \\ 6y-3y=-6+24 \\ 3y=18 \\ \text{divide both sides by the coefficient of y.} \\ \text{The coefficient of y is 3. Thus,} \\ y=(18)/(3)=6 \end{gathered}]()
Step 3:
Substitute the value of y in either equation 1 or 2.
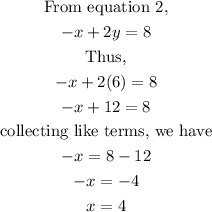
Thus, the values of (x, y) are (4, 6)