Answer
D. 6
Step-by-step explanation
Given that:
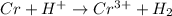
What to find:
The coefficient of H⁺ when the given equation is balanced with the smallest possible integer coefficients.
Solution:
The given equation is an example of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction
The first step is to identify the half equations:
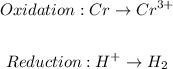
The next step is to balance the half equations molecularly follow by balancing the charge:
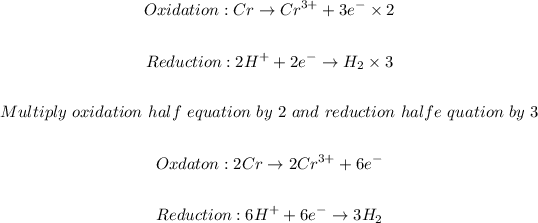
The final step is to combine the half equations and simplified:
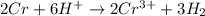
Therefore, the coefficient of H⁺ in the balanced equation above is 6.
The correct answer is D. 6