let's find the components for the initial velocity
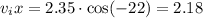
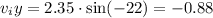
then for the final velocity
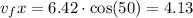
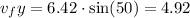
The table that agrees with the problem is A)
Then for the acceleration, we will use the next formula
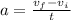
for the acceleration in x
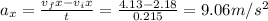
then for the acceleration in y
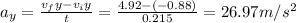
then we calculate the magnitude
![a=\sqrt[]{9.06^2+26.97^2}=28.45\text{ m/s}^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/1gq44etfacq19qn00ew9adpadee24brm13.png)