Answer:
• In order to understand this, we need to know that an inverse trigonometric function “undo” what the original trigonometric function
• e.g Trig function : inverse of trig. function .
Explanations :
(a) Inverse sine parent function:
The inverse y = six x parent function will be
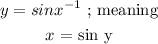
• y = sinx ^-1 , has domain at [-1;1] and range at (-/2; /2)
(b)Inverse cosine parent function
the inverse of y = cos x parent function will be :
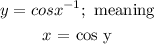
• y = cosx^-1 , has domain at [-1;1] and range at (0;)
(c)Inverse tangent parent function
The inverse of y = tan x parent function will be :
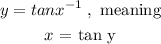
• y = tanx^-1 has domain at (-∞;∞) and range at (- /2 ; /2)
see the graphs below that shows the asympotes of the trigonometric function.