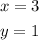Solution:
Given the simultaneous equations:
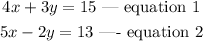
To solve for x and y, using the elimination method, we have
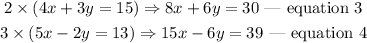
Add up equations 1 and 2.
thus, this gives
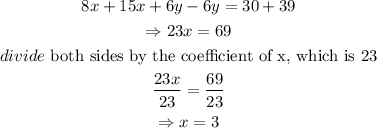
To solve for y, substitute the value of 3 for x into equation 1.
thus, from equation 1

Hence, the solution to the equation is