To sketch the graph, we need to find the x-intercepts and y-intercepts.
To find the x-intercepts we solve the equation when y = 0.
That is

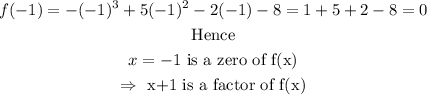
Next, we find the result of :
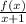
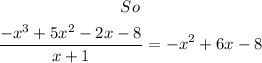
Now we solve
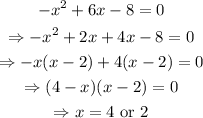
So the zeros of f(x) are -1, 2, and 4
Next, we find the stationary points.
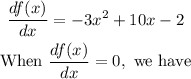
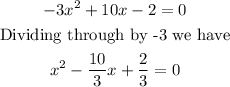
![\begin{gathered} (x-(5)/(3))^2-(-(5)/(3))^2-2=0 \\ \Rightarrow(x-(5)/(3))^2=2+(25)/(9)=(43)/(9) \\ \Rightarrow x=\frac{5\pm\sqrt[]{43}}{3} \\ \Rightarrow x=2.55\text{ or }0.78 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ytxuxu89diuedmd7dvq37teujfleq94k19.png)
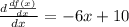
At x = 2.55
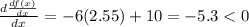
Hence we have a maximum point at x = 2.55
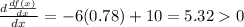
Hence, there is a minimum point at x = 0.78
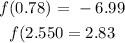

This implies that
f is increasing on the intervals (–∞, 1/3) and (3, ∞)