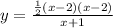Given:
• Vertical asymptote at : x = -1
,
• Double zero at: x = 2
,
• y-intercept at: (0, 2)
Let's create the equation for the rational function using the given properties.
Since the vertical asymptote is at x = -1, to find the deominator of the equation, equate the vertical asymptote to zero.
Add 1 to both sides:
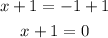
Therefore, the denominator of the function is ==> x + 1
Since it has a double zero at x = 2, we have the factors:
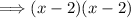
We now have the equation:
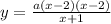
Also, the y-intercept is at: (0, 2)
To find the value o a, substitute 2 for y and 0 for x then evaluate:
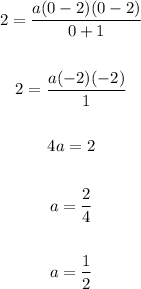
Therefore, the rational function is:
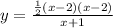
ANSWER: