Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the ∆°H for the reaction
Mathematically, to get this, we have to subtract the change in enthalpy of the reactants from that of the product
However, we shall not be considering the enthalpy values for single element molecules like hydrogen molecule and oxygen molecule
From the later reactions and values given, we can get the values for carbon (iv) oxide and Ethanol
For Carbon (iv) oxide, we have it as:

For Ethanol, we need to get the value for water
We have that as follows:
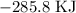
For ethanol, that would be: Let us label it e
![undefined]()