Answer:
a) pH= 13.3
b) pOH= 0.7
c) [H+]= 5.01*10^-14M
d) [OH-]= 0.2M
Step-by-step explanation:
The formula of sodium hydroxide is NaOH. In the molecule there are Na+ ions and OH- that dissociates like this:
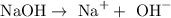
That means that 1 mole of NaOH dissociates into 1 mole of Na+ ions and 1 mole of OH-.
So, for a 0.2M solution, 0.2 moles of NaOH will dissociate into 0.2 moles of Na+ ions and 0.2 moles of OH-.
d) [OH-]
From the dissociation of NaOH we know that the concentration of OH- is [OH-]=0.2M.
b) pOH
With the concentration of OH-, we can calulate the pOH:
![\begin{gathered} pOH=-log\lbrack OH^-] \\ pOH=-log(0.2) \\ pOH=0.7 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/jnxglkctobt7r3zrxo6pvxpi9yv2itj85y.png)
So, the pOH is 0.7.
a) pH
Knowing the pOH and the following formula, we can calculate the pH of the solution:
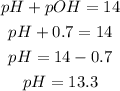
The pH of the solution is 13.3.
c) [H+]
Now that we know thw pH of the solution, we can calculate the concentration of H+:
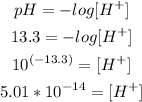
So, the concentration of H+ is 5.01*10^-14M.