Recall the definition of the sine of an angle on a right triangle:
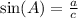
On the other hand, according to this diagram, the values for tan(A) and cos(A) are given by:
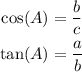
Since 180≤A≤270, the right triangle that corresponds to the angle A on the coordinate plane looks as follows:
Where a and b are negative distances.
Since sin(A)=-4/7, we can assume that a=-4 and c=7. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the exact value of b:
![\begin{gathered} a^2+b^2=c^2 \\ \Rightarrow(-4)^2+b^2=7^2 \\ \Rightarrow16+b^2=49 \\ \Rightarrow b^2=49-16 \\ \Rightarrow b^2=33 \\ \Rightarrow|b|=\sqrt[]{33} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/u6kd3ua89ndljqlyrq8k4dsznbbmxjmvbs.png)
We know that b should be negative. Then:
![b=-\sqrt[]{33}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/zlpas6k4bi52fmnmbdqbow659vrz22trgc.png)
Substitute b=-sqrt(33) and c=7 to find the exact values for cos(A) and tan(A):
![\begin{gathered} \cos (A)=-\frac{\sqrt[]{33}}{7} \\ \tan (A)=\frac{-4}{-\sqrt[]{33}}=\frac{4\cdot\sqrt[]{33}}{33} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/p3e7xecpv75apesfehouhbmjl59tlqxwid.png)
Therefore, the exact values for cos(A) and tan(A) are:
![\begin{gathered} \cos (A)=-\frac{\sqrt[]{33}}{7} \\ \tan (A)=\frac{4\cdot\sqrt[]{33}}{33} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/3g61y8w9wbsf2eeoiaqv9u8dymg7uts318.png)