We are told that we must assume that the gas behaves as an ideal gas in order to apply the following equation:
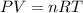
Where,
P is the pressure of the gas, 0.9801atm
V is the volume of the gas, 13mL=0.013L
R is a constant, 0.08206 atm-L/mol-K
T is the temperature of the gas, 22°C=295.15K
Now, we will clear the moles of the gas, n and we replace the known data:
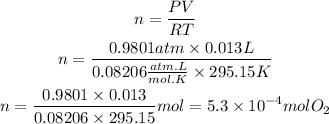
now, to have the mass of the gas, we will use the molar mass. In this case, the molar mass of O2=31.999g/mol
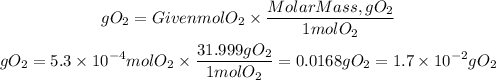
The grams of O2 produced in the reaction are 1.7x10^-2 g of O2