We are given a right-angled triangle.
Two of the side lengths are given and the third is missing.
We can us the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side of the triangle.
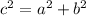
Where c is the longest side, a and b are the shorter sides of the triangle.
![\begin{gathered} c^2=a^2+b^2 \\ x^2=7^2+24^2 \\ x^2=49^{}+576 \\ x^2=625 \\ x^{}=\sqrt[]{625} \\ x^{}=25 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/5lnfe586c35pczcl8lge1tt31f98v15dzk.png)
Therefore, the missing side of the triangle is 25