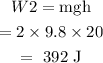Given the mass of the object, m = 2 kg
Distance between point A and B, h= 20 m
(a) To find work done in moving the object from A to B
Work done is
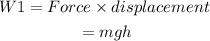
Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity whose value is 9.8 m/s^2.
Substituting the values, we get
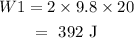
(b) To find work done in moving the object from A to C
Gravitational force is a conservative force and work done depends only on the initial and final position and not on the path.
So, the work done will be