Given in the question:
a.) Random guesses are made for six multiple-choice questions.
b.) There are five choices for each question.
c.) There are n equals six trials each with the probability of success (correct) given by P equals 0.20.
We will be using the Binomial Probability Formula:
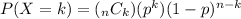
Where,
n = Number of trials = 6
P = Probability of success = 0.20
X = Correct answers
Let's evaluate the definition of binomial probability at k = 0 since we are tasked to find the probability of no correct answers.
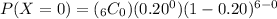
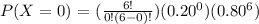
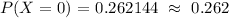
Therefore, the probability of no correct answers is 0.262 or 26.20%.