For the first equation:
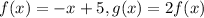
That's a vertical stretch by 2. If you change f(x) for 'y' you'll see that more clearly:
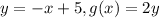
All 'y' coordinates of the function are now twice as before. This means that the function is stretched vertically.
For the second:
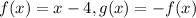
We'll change f(x) for 'y' too:
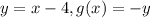
That is a reflection over the x axis. This is because in order to go from y to -y all 'y' coordinates of the points on the function have to change from possitive to negative and from negative to possitive. In a graph: