To calculate the maximum distance that the ball takes, we can use the first and second derivatives of y to find out this. We have:
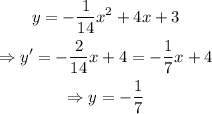
Using the second derivative criterion, we have that y'' < 0, therefore, we have a maximum in the root of the first derivative. For that, we get the following:
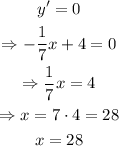
Therefore, at x=28 is where the maximum distance is. Now we only substitute x=28 in y to find out:
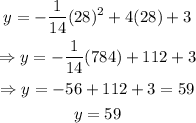
Finally, we have that the ball will go 59 feet from the child