Given:-
An reatacngle with a half sphere at one side.
To find:-
The perimeter of the given image.
Now we are going to find the perimeter of the half sphere. The formula to find half sphere is,
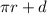
Where r is radius and d is diameter.
The radius of the sphere is 2.5 and the diameter is 5. Substituing the values we get,
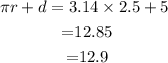
Now we find the perimeter of the rectangle below. we get,
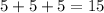
Now to get the total perimeter we need to add both the values. so we get,
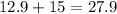
So the required perimeter is 27.9