Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
In problem 5, we can see that there is a right triangle with legs x and 16 and a hypotenuse equal to (x + 8).
So, by Pythagorean theorem, we can write the following equation
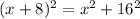
Now, we can expand the left side
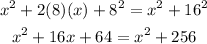
Then, subtract x² from both sides
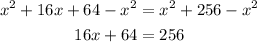
Subtract 64 from both sides
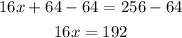
Finally, divide by 16
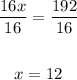
Therefore, the value of x is 12