Answer:
0.0899 moles of oxygen (O2).
Step-by-step explanation:
What is given?
Mass of sodium oxide (Na2O) = 11.15 g.
Molar mass of Na2O = 62 g/mol.
Step-by-step solution:
First, let's state the balanced chemical equation:
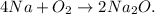
Let's calculate the moles of Na2O that are in 11.15 g of Na2O, using its molar mass:
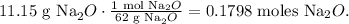
Now that we have the moles of Na2O, let's do the stoichiometry: you can see in the chemical equation that 1 mol of oxygen (O2) reacted produces 2 moles of Na2O, so by doing a rule of three based on this data, the calculation will look like this:
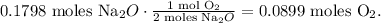
The answer is that we need 0.0899 moles of oxygen (O2) to produce 11.15 g of sodium oxide.