Given that the velocity at any time t is
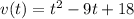
Also, the time interval is from t = 0 to t = 8 seconds
The position at time t = 0 s is s(0) = 1 m towards right of zero.
The initial time is t = 0 s, so the initial velocity will be
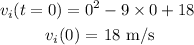
The final time is t = 8 s, so the final velocity will be
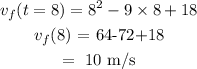
The average velocity will be
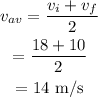
Thus, the average velocity is 14 m/s.
Part II:
The instantaneous velocity at time t =5 s will be
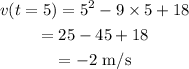
The instantaneous speed is the magnitude of instantaneous velocity.
Thus, the instantaneous speed will be 2 m/s.
Part III:
The particle will move towards the right when v(t) > 0
The time intervals will be
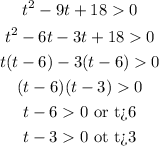
Thus, time intervals are t > 3 and t > 6 when the particle is moving towards the right.
Part IV :
The particle will move faster if the acceleration, a(t) > 0
The particle will slow down if the acceleration, a(t) < 0
So, first, we need to find the acceleration, it can be calculated as
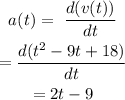
For the particle moving faster,
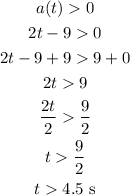
For particle slowing down,
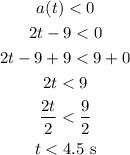
The total distance can be calculated as
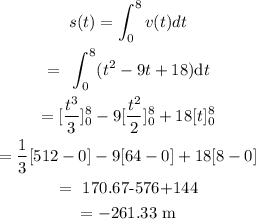
Here, the negative symbol indicates it is towards the left from zero.