The given exponential function is
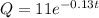
The form of the exponential continuous function is
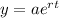
a is the initial amount (value y at t = 0)
r is the rate of growth/decay in decimal
Compare the given function by the form
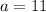
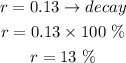
a)
The value of Q at t = 0 is 11 and the decay rate is 13%
The initial value of Q is 11
The continuous decay rate is 13%
From the graph
To find the value of t when Q = 2
Look at the vertical axis Q and go to the scale of 2
Move horizontally from 2 until you cut the graph
Go down to read the value of t
The value of t is about 13
b)
At
Q = 2
t = 13
c)
Now, we will substitute Q in the function by 2
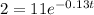
Divide both sides by 11
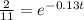
Insert ln on both sides
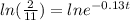
Use the rule
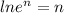
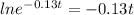
Substitute it in the equation

Divide both sides by -0.13
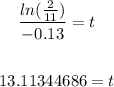
At
Q = 2
t = 13.11344686