The heat Q needed to increase the temperature of a sample with mass m and specific heat c by an amount ΔT is:
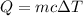
On the other hand, a change in temperature in Farenheit is related to a change in temperature in Celsius as:
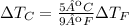
Replace m=7.3kg, c=385J/(kgºC), as well as the final and initial temperatures to find the heat required to raise the temperature of the sample of Copper:
![Q=(7.3\operatorname{kg})(385\frac{J}{\operatorname{kg}ºC})(865ºF-38ºF)]()
Since the specific heat is given in units of Joules per kilogram per degree Celsius, introduce the factor 5ºC/9ºF to write the change in temperature in degrees Celsius:
![\begin{gathered} Q=(7.3\operatorname{kg})(385\frac{J}{\operatorname{kg}ºC})(865ºF-38ºF)*(5ºC)/(9ºF) \\ =1,291,268.611\ldots J \\ \approx1.3*10^6J \end{gathered}]()
Therefore, the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of the 7.3 kg of Copper sample from 38ºF to 865ºF, is 1.3*10^6 Joules.