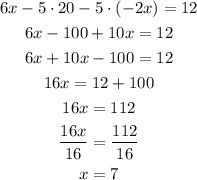Given the equation system:
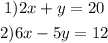
To solve the system and determine the value of x, first step is to write one of the equations in terms of y:
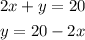
Then replace this expression in the second equation
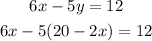
Now that you have an expression with only one unknown, x, you can calculate its value.
Solve the parenthesis using the distributive property of multiplication