A conditional statement can be written as:

An example of this in real life is:
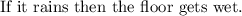
In this case:
p = it rains
q = the floor gets wet
The converse of that conditional is:
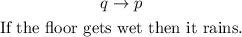
Notice that the conditional being true doesn't mean necessarily that its converse is true. For example, every time it rains the floor gets wet can be true, but the floor could get wet for other reasons, so the converse would not be true.
Also, the inverse of that conditional is:
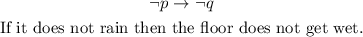
As we see, the inverse of a true conditional statement is not necessarily true.
And the contrapositive of that conditional statement is:
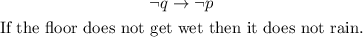
Now, the contrapositive of a true conditional statement is always true. Notice that if every time it rains the floor gets wet, the only explanation for the floor not getting wet is that it does not rain.